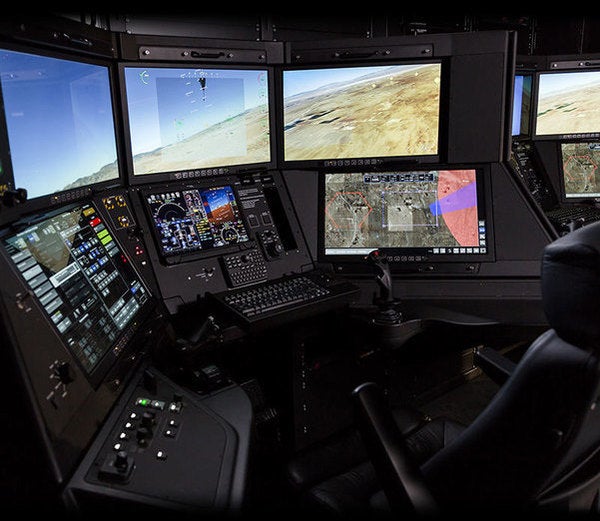

General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI) has successfully completed the first test of its certifiable (STANAG 4671-compliant) ground control station (C-GCS).
The C-GCS was used to fly GA-ASI’s MQ-9B SkyGuardian remotely piloted aircraft (RPA).
The trial, which was conducted from Yuma, Arizona, US, successfully tested and evaluated the flight critical functions of the unmanned aerial vehicle, including hold modes, landing gear, flap operation, and hand-flying of the aircraft.
GA-ASI chief executive officer Linden Blue said: “This marks a major milestone for the C-GCS. We continue on a path towards integrating RPA into non-segregated national and international airspace, where they can fly safely alongside commercial aircraft.
“To achieve that goal, we are producing STANAG-compliant GCSs in addition to STANAG-compliant SkyGuardian aircraft.”
GA-ASI’s C-GCS features the same flight management system, cockpit displays and navigation guidance as available on modern corporate and commercial aircraft.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalDataIn addition, the certifiable control station enables weapons and payload control for SkyGuardian, while its hardware and software architecture offers separation of flight and mission-critical functions.
This allows for mission software upgrade without affecting flight critical software.
The mission human machine interface (HMI) has been specially designed to ensure the provision of situational awareness on a single tactical situation display.
The upcoming test scheduled for the MQ-9B SkyGuardian C-GCS includes full launch and recovery, HMI enhancements, mission-critical functions and satellite communication (SATCOM) datalink testing.
On 26 September, the company successfully completed the maiden flight test of its second MQ-9B SkyGuardian RPA, the YBC02, at the Laguna Army Airfield in Yuma Proving Grounds in the US.



