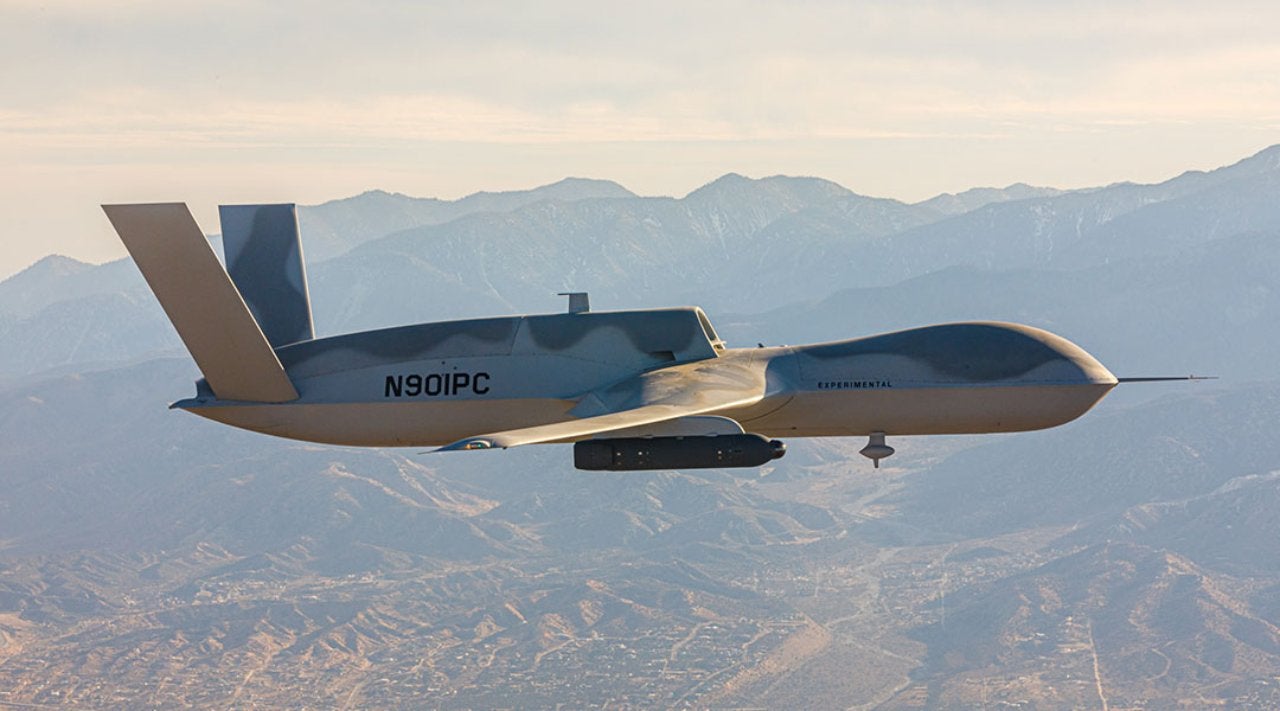

General Atomics Aeronautical Systems (GA-ASI) has conducted a flight test of an Avenger remotely piloted aircraft (RPA) with new technology to boost autonomous sensing capabilities.
During the flight test, the Avenger RPA was equipped with a Lockheed Martin Legion Pod, a multi-function sensor system.
According to the Lockheed Martin website, the sensor system supports collaborative targeting operations in radar-denied environments.
For the test, the Legion Pod was equipped with an infrared search and track (IRST) system that can detect and track air-to-air targets in radar-denied environments.
GA-ASI Strategic Development vice-president JR Reid said: “Our flight demonstration revealed the quick reaction capabilities of the Avenger RPA. From software and hardware architecture implementation to sensor integration, the Avenger is a great platform for delivering critical capabilities.”
Lockheed Martin Missiles and Fire Control Fixed Wing Sensor Programs director Kenen Nelson said: “The successful integration of Legion Pod on the Avenger RPA is a testament to the flexibility of the Legion Pod system from a fighter aircraft to an unmanned aircraft, which means Legion Pod has proven its capabilities can assist our warfighter and keep them ahead of threats.
US Tariffs are shifting - will you react or anticipate?
Don’t let policy changes catch you off guard. Stay proactive with real-time data and expert analysis.
By GlobalData“We are excited to see how our IRST21 systems will be integrated on other unmanned platforms.”
GA-ASI now plans to conduct additional follow-on flights this year.
Developed with internal funding, Predator C Avenger is developed to provide the operator with an expanded quick-response armed reconnaissance capability.
Last month, GA-ASI completed the full-scale static (FSS) testing on the MQ-9B RPA wing.



