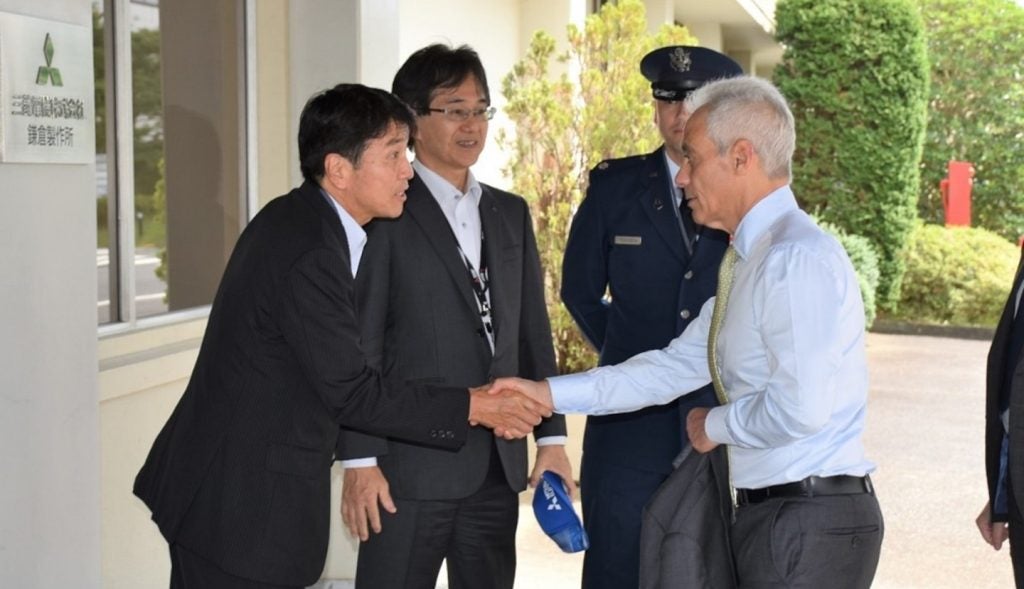
US Ambassador to Japan, Rahm Emanuel, visited the Quasi-Zenith Satellite System Hosted Payload (QZSS-HP) facility this month in Kamakura, Japan.
The QZSS-HP is a constellation comprising four geosynchronous satellites designed to improve conventional US-operated global positioning systems (GPS). Plans are in the making to expand the system to 11 satellites QZSS-HP marks a unique pathfinding national security space co-operation initiative between the United States and Japan.
Space Systems Command (SSC), a US Space Force (USSF) logistics division, recently delivered two sensor payloads to be integrated into two new Japanese QZSS satellites that will be launched on a Japanese-developed launch vehicle as part of the USS-Japan mission.
The visit took place at Mitsubishi Electric Kamakura Works. Emanuel was on hand to see the first payload integrated with the first host satellite, QZS-6, followed by a briefing on the mission.
SSC has supported the QZSS-HP programme as a rapid acquisition and pace-setting partnership effort with Japan since its inception in 2018 and the historic December 2020 memorandum of understanding between Japan's Space agency and the USSF that allowed the two countries to break ground and begin execution.
QZSS situational awareness
According to the US Department of Defense’s (DoD) fiscal 2023 budget documents, the QZSS payloads will “enhance capabilities over the Eurasian theatre and facilitates resilient capabilities in the Space Surveillance Network (SSN).” The SSN is the US military’s network of ground-based radar and telescopes for space domain awareness, along with the six geosynchronous space domain situational awareness satellites.
“[A]llied participation allows us to defray costs, incorporate different perspectives and different capabilities.
“It also makes our adversaries have to look at situations differently. That is truly the benefit of having allied, like-minded partners coming together and saying, ‘This is what’s best for our mutual defence and assurance,” F Schnell, director of acquisition, SSC Space Domain Awareness Delta stated.
Extended deterrence dialogue
On the 26-27 June, the US and Japan convened its extended deterrence dialogue (EDD) at the Whiteman Air Force Base, Missouri. The United States and Japan established the EDD in 2010 as an enduring venue to discuss ways to sustain and strengthen extended deterrence, which is at the core of the US-Japan Alliance.
The QZSS-HP programme works at th heart of this deterrence alliance, where the nations share critical intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance data in the system’s coverage across the Eurasian theatre.
Moreover, the programme’s expansion demonstrates the alliance’s commitment to “optimising the Alliance’s force posture and activities to bolster deterrence effectiveness,” according to the US Department of Defense.