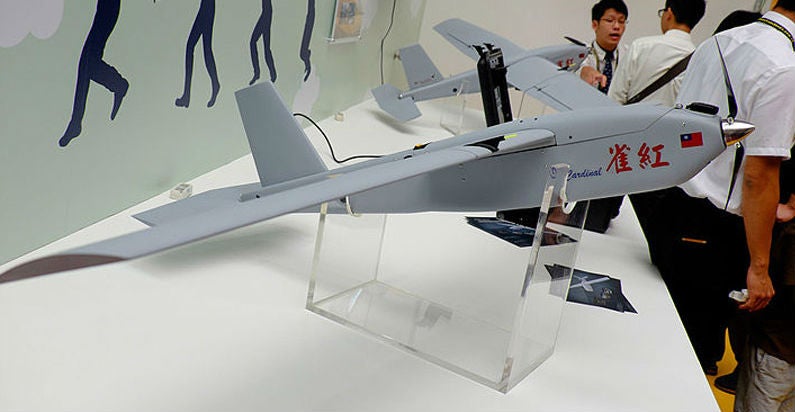
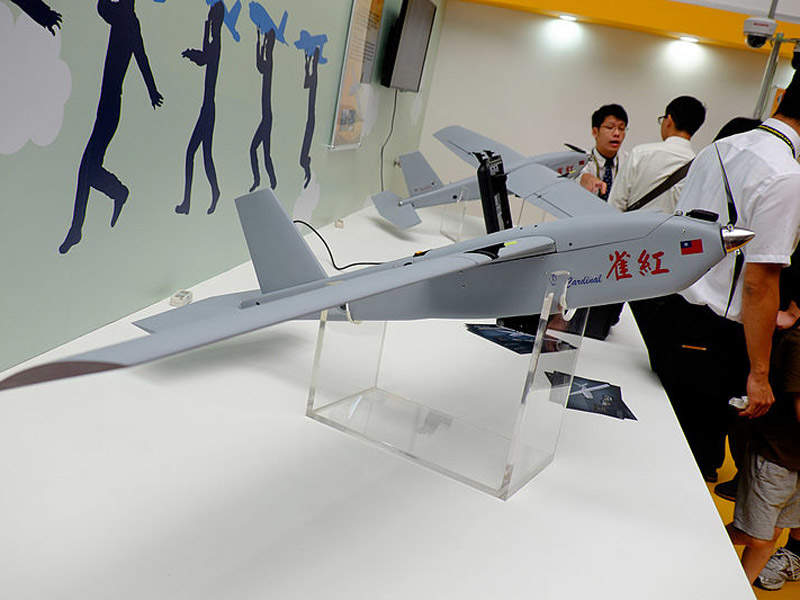
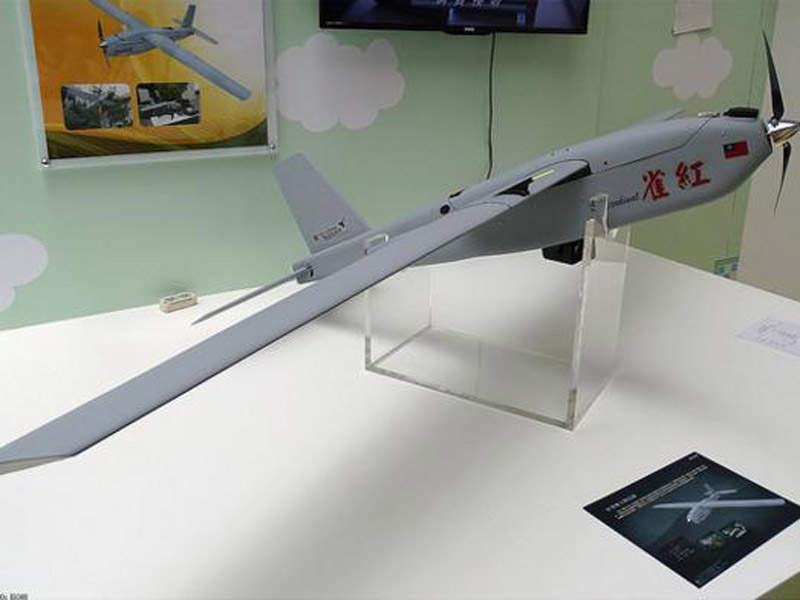
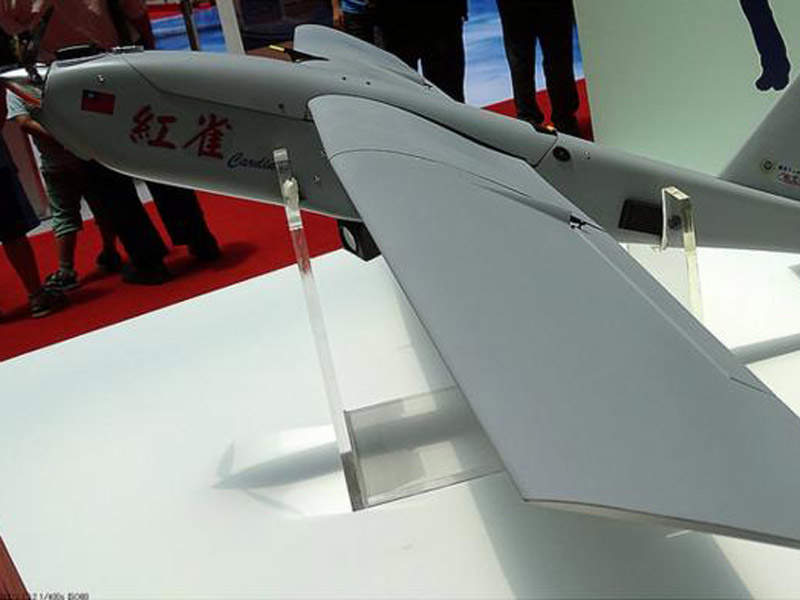
Cardinal II is a small unmanned aircraft system (UAS) designed to provide combat troops and police forces with intelligence gathering, surveillance, tactical reconnaissance and target acquisition capabilities.
The UAS is developed by Aeronautical Systems Research Division (ASRD) of Taiwan-based National Chung-Shan Institute of Science and Technology (NCSIST), based on the Cardinal I air system.
Development of the Cardinal air system began in 2009 and a model of the UAS was displayed at the Taipei International Aerospace and Defense Industry Exhibition held in Taiwan in August 2013. Cardinal II was demonstrated at ASRD in Taichung and a mock-up of the drone was recently exhibited at the Bahrain Air Show held in January 2016.
The unmanned aircraft system can be configured for civil applications such as monitoring of roadway traffic, disaster relief and rescue operations, environmental monitoring, and aerial survey of forests and mountain regions.
Orders and deliveries
The Republic of China Marine ordered five units of Cardinal II UAS, which are scheduled for delivery in 2016.
Cardinal II UAS design and features
The Cardinal II unmanned aircraft system includes an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV), digital data link, automatic tracking antenna, and ground control system.
Weighing roughly 5.5kg, the UAV can be quickly disassembled and carried in a portable backpack. It is 1.9m-long, 1.3m-wide and 0.35m-high, and features a modular design. It is outfitted with propulsion system, flight control computer, autopilot, global positioning system (GPS), and payloads.
The air vehicle is launched by hand and recovered by parachute. It can also be landed using glide landing method. The tail section, fitted with one vertical fin and two horizontal stabilisers, provides increased flight speed.
The drone is capable of flying autonomously and by remote control. Together with GPS guidance, the autopilot allows the UAV to fly based on pre-programmed flight path in the autonomous mode of operation enabling it to return home and land safely even in the event of communications failure.
Payloads and sensors aboard Cardinal II air vehicle
A 360° electro-optical (EO) or infrared (IR) imaging camera system is mounted under the fuselage of the UAS. It is used to capture high-resolution imagery and video in all lighting conditions.
The UAV is integrated with a digital data link to transmit real-time imagery and telemetry data acquired by the onboard payloads to the ground segment and to receive mission commands from the operator.
Ground control station
The UAV’s flight and payloads can be remotely-controlled by two operators from the ground control station using a guidance and control system. The digital maps and flight parameters are displayed in real-time on large screens.
The omni-directional tracking antenna is used to track target objects automatically in all horizontal directions. A portable video receiver module in the ground segment receives real-time full-motion video from the drone.
Performance of the unmanned aerial vehicle
Powered by a brushless electric motor, the Cardinal II UAV is able to fly at a cruise speed of 55km/h. The motor drives a two-blade propeller mounted in the nose. The UAV has a range of 8km and a flight time of one hour.
The unmanned aircraft system can be deployed from naval ships to provide troops with precise target location.
The Global Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) Market 2011-2021
This project forms part of our recent analysis and forecasts of the global unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) market available from our business information platform Strategic Defence Intelligence. For more information click here or contact us: EMEA: +44 20 7936 6783; Americas: +1 415 439 4914; Asia Pacific: +61 2 9947 9709 or via email.