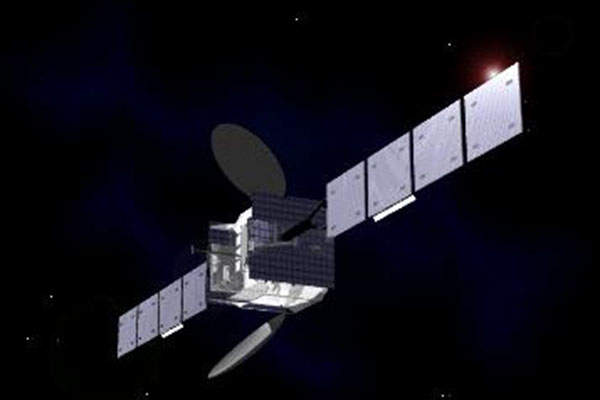
The Göktürk-1 reconnaissance and Earth observation satellite was built for the Turkish Ministry of National Defence by satellite services provider Telespazio in cooperation with Turkish Aerospace Industries (TAI) and Thales Alenia Space.
The satellite provides high-resolution aerial images of the Earth for a wide range of military and civilian applications, including reconnaissance, homeland surveillance, intelligence, environmental monitoring, forest control, and cadastral surveys.
It also identifies illegal construction sites, crop management, damage assessment after natural disasters, and management of natural resources.
The Göktürk-1 satellite was launched by the Vega launch vehicle from the Guiana Space Center, French Guiana in December 2016. It is placed into a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 700km and has a design life of seven years.
The Göktürk Earth observation satellite series also includes Göktürk-2 and Göktürk-3.
Development of Göktürk Earth observation satellite
KazEOSat-1 is the first Earth observation satellite from Kazakhstan, which launched into a low Sun-synchronous orbit in April 2014.
The Ministry of National Defense of Turkey’s Undersecretariat of Defense Industries signed a contract with Telespazio to build the Göktürk observation satellite system in July 2009. The system comprises an Earth observation satellite fitted with high-resolution optical sensors, ground control segment, and a satellite assembly, integration and test centre.
Telespazio, a joint venture (JV) between Finmeccanica and Thales, is the prime contractor for the Göktürk satellite programme. The JV entered design and construction phase in September 2010. It was responsible to build the entire ground segment and provide services during satellite launch. It also supported early orbit operations and test phase.
Thales Alenia Space supervised the construction of the satellite bus and development of the satellite assembly, integration and test centre in Turkey, which is operated by TAI.
The Göktürk satellite system components were supplied by the local industrial partners in Turkey, including Aselsan, Tubitak Uekae, Roketsan and TR Tecnoloji. The local partners also supported construction of the satellite integration centre, remote sensing data processors, data acquisition station, and mission planning systems.
Arianespace was contracted by Telespazio to provide Vega light launcher for the launch of the Göktürk-1 Earth observation satellite in June 2013. Aselsan subcontracted SDT to provide satellite ground station user services.
Göktürk-1 satellite’s features and communications
Göktürk-1 Earth observation satellite has a launch weight of 1,100kg. It is equipped with two deployable fixed solar arrays and batteries. The spacecraft has a signal-to-noise ratio of more than 100.
The satellite image data is transmitted to the ground segment over S-band and X-band links. It is also capable of supplying images of the Earth in all-weather conditions during day and night.
The satellite uses a key management system and cryptosystems developed by Tubitak for the secure transmission of data.
G-DCUA ground station crypto module encrypts satellite commands received from the ground station. It also decrypts the encrypted satellite image data, which is then processed by the ground station.
S-DCUA satellite cryptosystem is used to decrypt and verify commands and transmit them to the satellite. It also encrypts image data before transmitting it to the ground segment.
Payloads attached to the Göktürk-1 Earth observation satellite
The Göktürk-1 satellite is equipped with an electro/optical (E/O) camera system for capturing high-quality imagery of the Earth from any location, with a ground sample distance of 0.5m. The camera system operates in various display modes such as point, strip, wide-area and stereo.
Göktürk satellite’s ground segment
The ground station controls the satellite’s missions as well as in-orbit operations. It receives image data and sends commands to the satellite using a 7.3m fixed antenna with S/X-band feed and a 5.4m S/X-band mobile antenna. It also performs acquisition, processing and distribution of data received from the satellite.
Vega launch vehicle
Operated and marketed by Arianespace, the Vega launch vehicle successfully performed a qualification flight in February 2012. It is intended to launch small to medium-sized satellite payloads. It has a length of 29.9m, diameter of 3.02m, height of 30m, with a lift-off mass of 137t and the capacity to carry payloads of up to 1,500kg.
The launch vehicle comprises four stages. The first three stages are powered by solid propellant motors P80, Zefiro 23, and Zefiro 9. The upper stage, the Attitude and Vernier Upper Module (AVUM), is powered by N2O4/UDMH propellant.