
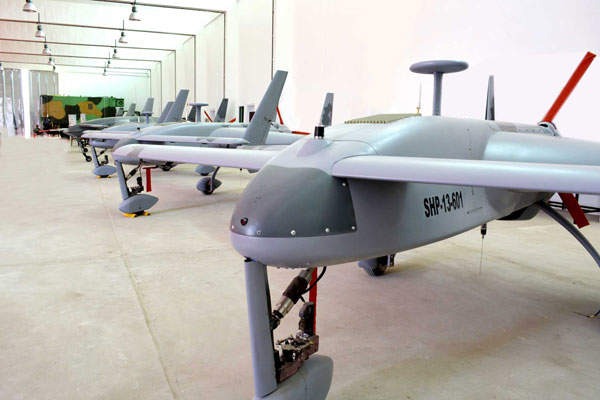
Shahpar is a tactical unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) designed, developed and manufactured by Global Industrial Defence Solution (GIDS) for the Pakistan Armed Forces. The UAV can be deployed for real-time reconnaissance and surveillance, monitoring, target acquisition, situational awareness and disaster management missions.
The Shahpar UAV was displayed at the International Defence Exhibition and Seminar (IDEAS) at Karachi Expo Centre in Pakistan in November 2012. It was also demonstrated at the International Defence Exhibition and Conference (IDEX) in Abu Dhabi, UAE, in February 2013.
The Pakistan Ministry of Defence (MoD) commissioned the first fleet of Shahpar UAVs into the Pakistan Army and Air Force in November 2013.
Shahpar UAV design and features
The medium range Shahpar UAV was indigenously developed in co-operation with the National Engineering and Scientific Commission (NESCOM), a civilian controlled scientific and research organisation of Pakistan.
The vehicle has a length of 4.2m and wing span of 6.6m, and is configured with canard foreplanes positioned in front of the wings. The maximum take-off weight of the UAV is 480kg.
Falco is a state-of-the-art medium-altitude endurance and tactical unmanned air vehicle (UAV) manufactured by the Italian sensors developer Selex Galileo.
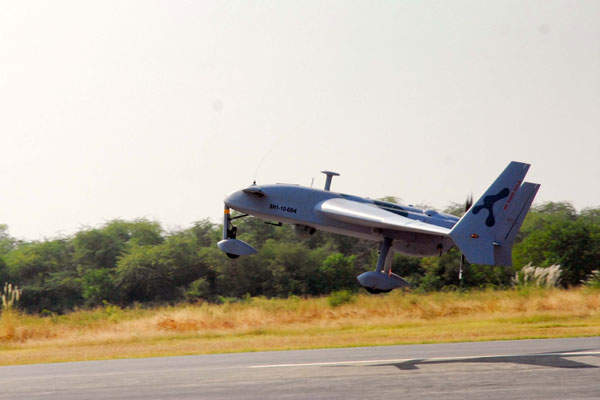
The UAV features autonomous take-off and landing capabilities. It can land on a runway independently or with the help of a manual pilot or parachute.
Payloads attached to the Shahpar UAV
Shahpar can be integrated with a variety of payloads to execute reconnaissance and surveillance missions during day and night environments. The vehicle is capable of carrying an optical payload of about 50kg.
Other payloads aboard the vehicle include mission planning, management and control, accurate lateral and longitudinal trajectory control, full mission debriefing and simulation, built-in data exploitation and dissemination systems.
The vehicle is also equipped with an autonomous global positioning system (GPS) based tracking and control system, with an option for manual control channel. It can carry additional payloads based on customer requirements.
The UAV has significantly reduced radar cross section (RCS) and features military standard hardware to a level of Environmental Standard 810F. It supports Motion Imagery Standards Board (MISB) compliant video format.
Sensors of the UAV from GIDS
The Shahpar UAV is equipped with the latest airborne imaging equipment (AIE), Zumr-I (EP) multi sensor turret that supports the improved local security and mobility of the UAV. The sensor systems include a high end thermal imaging camera, low-light and near infrared (IR) TV, and an eye safe laser range finder (LRF) with a range of around 20km.
The UAV is also fitted with Erica Plus, a high definition enhanced reconnaissance IR camera, and image processing system to provide extended visibility in harsh weather conditions.
The electro-optical (EO) / IR sensors allow Shahpar to provide the commanders with geo referenced and geo pointing imagery of terrestrial targets. The UAV transmits the captured data to the ground control station through the real-time data link with a range of 250km.
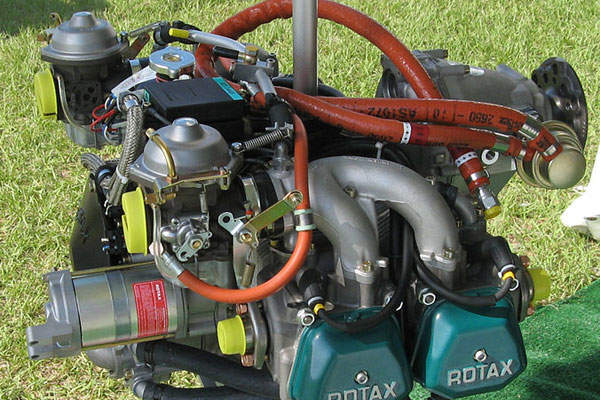
Engine and performance
The UAV is powered by a pusher-type four-stroke Rotax 912 ULS engine with four cylinders. The engine produces a power of 100hp.
Shahpar can fly at a cruise speed of 150kph (81kts) and can continuously operate for more than seven hours. The maximum operating altitude of the drone is 5,000m.
Key players involved with the Shahpar UAV development and manufacturing
The sensor systems of the UAV were built by Advanced Engineering Research Organization (AERO), a GIDS company, at its manufacturing plant near Islamabad. Another GIDS company, Xpert Engineering Services manufactured most of the components and payload systems of the UAV.





.gif)
